Hybrid
Important
The Hybrid deployment option requires an Enterprise plan.
Requirements
- You use
langgraph-cliand/or LangGraph Studio app to test graph locally. - You use
langgraph buildcommand to build image.
Hybrid
The Hybrid deployment option lets you manage the data plane in your own cloud, while we handle the control plane in ours. When using the Hybrid version, you authenticate with a LangSmith API key.| Control plane | Data plane | |
|---|---|---|
| What is it? |
|
|
| Where is it hosted? | LangChain’s cloud | Your cloud |
| Who provisions and manages it? | LangChain | You |
Architecture
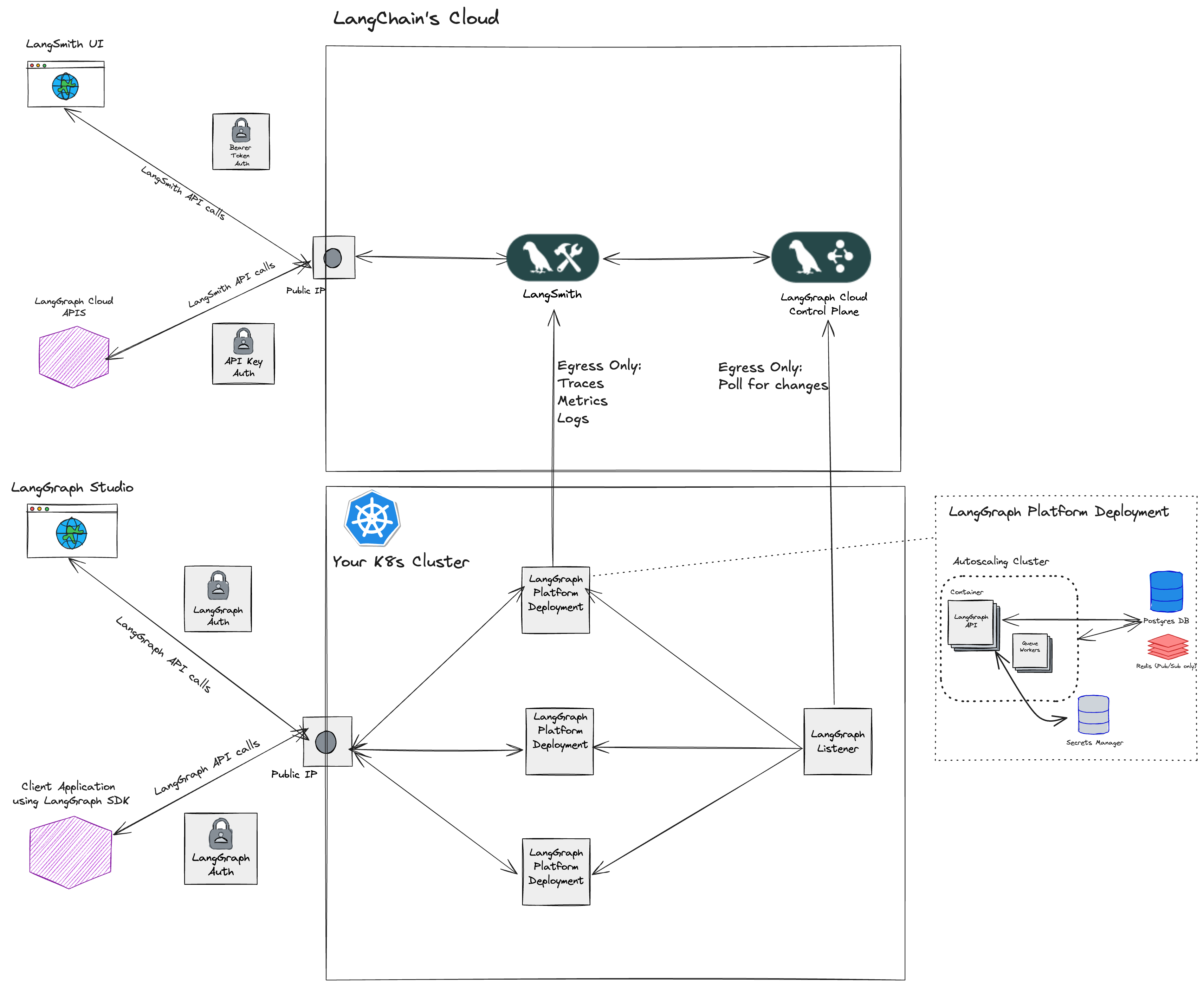
Compute Platforms
- Kubernetes: The Hybrid deployment option supports deploying data plane infrastructure to any Kubernetes cluster.
If you would like to deploy to Kubernetes, you can follow the Hybrid deployment guide.
Listeners
In a hybrid deployment, one or more “listener” applications can be deployed depending on the organization of LangSmith workspaces and Kubernetes clusters. Kubernetes cluster organization- One or more listeners can be deployed on a Kubernetes cluster.
- A listener can be configured to deploy to one or more Kubernetes namespaces in the cluster.
- The owner of the Kubernetes cluster is responsible for the optimal organization of listeners for their use case. This involves carefully planning how LangGraph Server deployments should be structured in advance.
- A workspace can have one or more listeners associated with it.
- LangGraph Server deployments in a workspace can only be deployed to Kubernetes clusters where all the workspace listeners are also deployed.
Use Cases
The following provides a non-exhaustive list of examples for configuring listeners based on the organization of your LangSmith workspaces and Kubernetes clusters. However, these are not strict requirements.Each LangSmith workspace deploys to a separate Kubernetes cluster
Example:- Kubernetes cluster
alphais for workspaceA - Kubernetes cluster
betais for workspaceB
Each LangSmith workspace deploys to a separate Kubernetes cluster, but “dev” workloads can be deployed to a shared Kubernetes cluster
In this use case, mulitple LangSmith workspaces deploy to a single Kubernetes cluster. Example:- Kubernetes cluster
alphais for workspaceA - Kubernetes cluster
betais for workspaceB - Kubernetes cluster
devis for workspacesAandB - Both workspaces have two listeners associated with them
- Kubernetes cluster
devhas two listener deployments
Deploy to one Kubernetes cluster, in one Kubernetes namespace
Example:- Kubernetes cluster
alphais for workspaceA - Kubernetes cluster
alphais for workspaceB
Deploy to one Kubernetes cluster, but in multiple Kubernetes namespaces
Example:- Kubernetes cluster
alphaand namespace1is for workspaceA - Kubernetes cluster
alphaand namespace2is for workspaceB

